Melanotan I Research Overview — α-MSH Analog and Melanocortin Pathway Studies
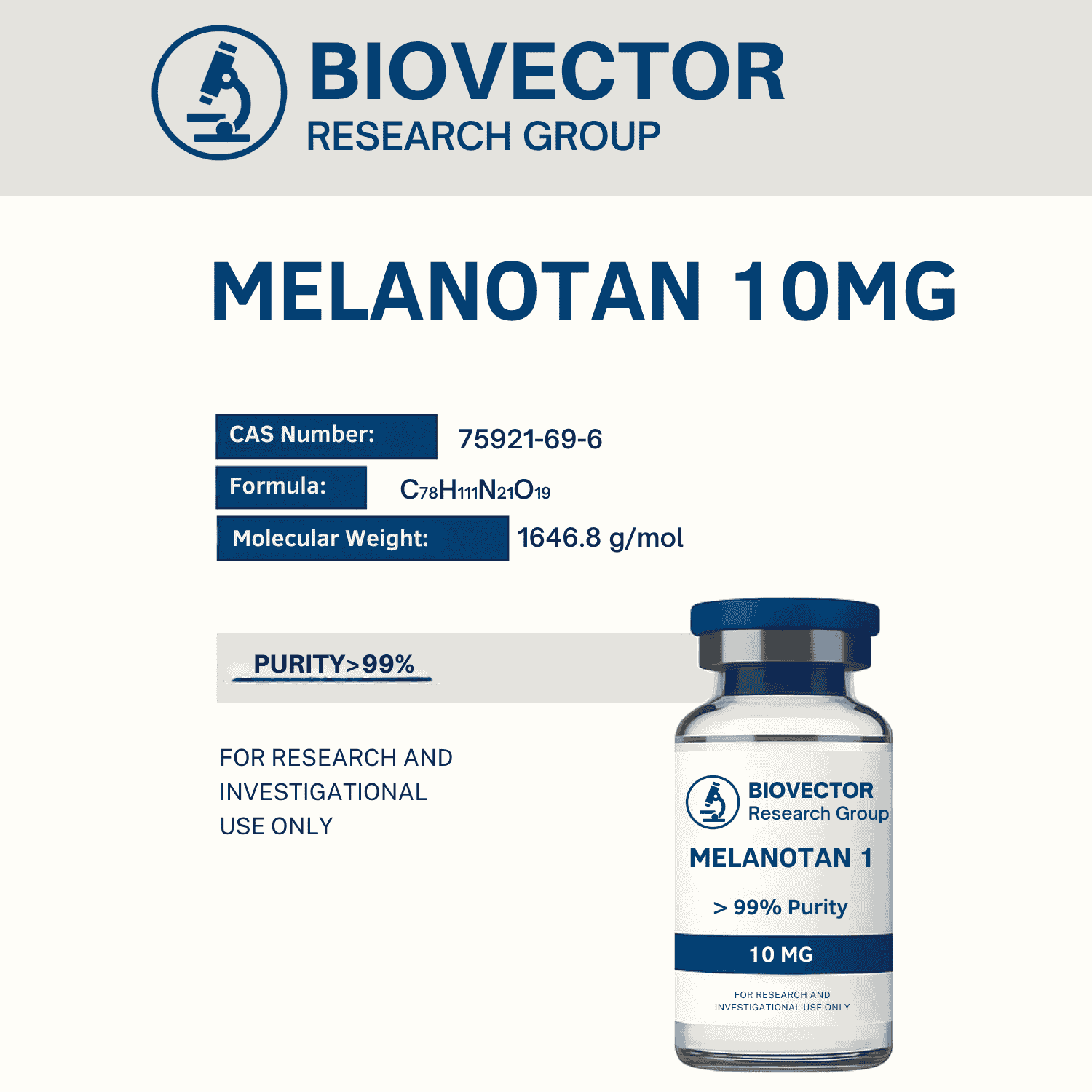
Disclaimer: This article is intended solely for laboratory and educational discussion. Melanotan I is provided for research use only and is not approved for human, veterinary, or diagnostic purposes. Melanotan I (also known as Afamelanotide or α-MSH analog) is a synthetic peptide derivative of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH). It acts as an agonist of the melanocortin-1 receptor (MC1R), which plays a role in melanin production and cellular signaling pathways related to oxidative stress and inflammatory modulation. (PubChem) Research on Melanotan I has focused on its ability to activate the MC1R pathway in controlled laboratory environments. Preclinical studies indicate that MC1R activation can enhance eumelanin synthesis and contribute to the understanding of pigmentation biology, DNA protection mechanisms, and photobiological responses. (PubMed) (NIH/PMC) Further studies have examined Melanotan I’s receptor selectivity and stability under physiological conditions, making it a valuable research tool in the study of melanocortin receptor pharmacodynamics and peptide structure–activity relationships. Ongoing in-vitro and animal model research continues to explore its influence on oxidative pathways and cellular protection responses. (PubMed Study)Key References
- PubChem Compound Summary — pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Melanotan-I
- Bohm et al., “Alpha-Melanocortin and MC1R Receptor Signaling,” Experimental Dermatology (2010) — pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20301523
- Schauer et al., “Pharmacology of Afamelanotide (Melanotan I),” Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences (2010) — pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20414042
- Singh et al., “Melanocortin receptor agonists and their structure-activity relationships,” Journal of Peptide Science (2014) — pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25196702
BioVector Research Group supplies Melanotan I for controlled laboratory and research purposes only. Not for human use or clinical application.